The Way A Network Is Configured Is Called The _____.
circlemeld.com
Sep 11, 2025 · 7 min read
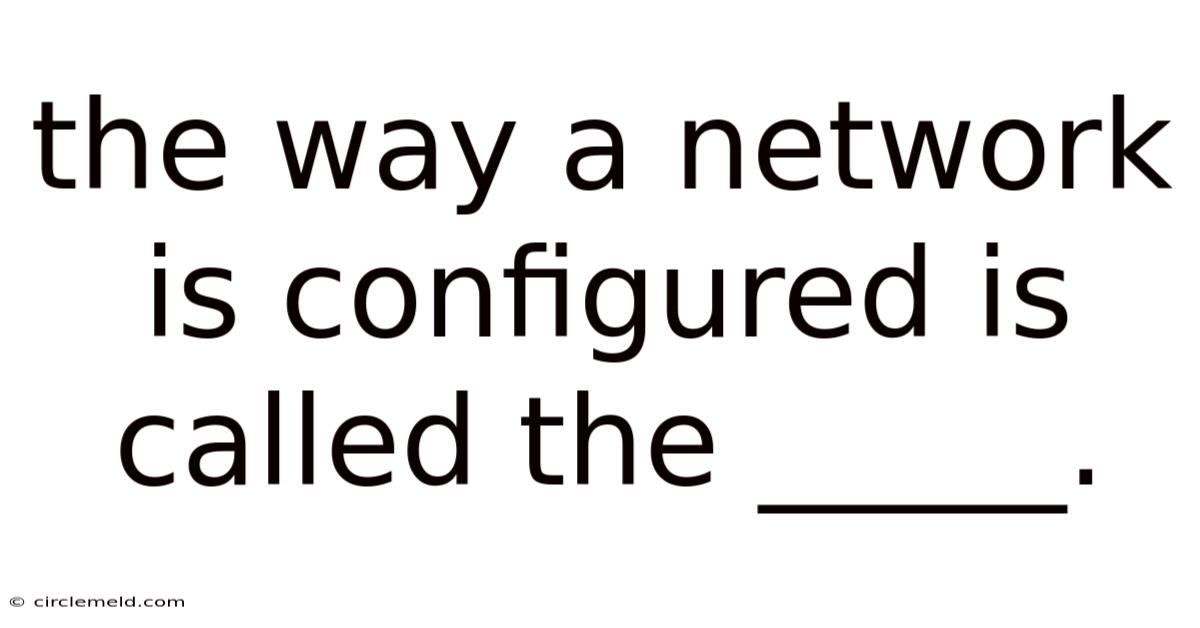
Table of Contents
The Way a Network is Configured is Called the Network Topology
The way a network is configured is called its network topology. Network topology refers to the physical or logical layout of nodes (computers, printers, servers, etc.) and connections in a network. Understanding network topology is crucial for network administrators, as it directly impacts performance, scalability, reliability, and security. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of network topologies, their advantages and disadvantages, and factors to consider when choosing the right topology for your network.
Understanding Network Topologies: A Foundation for Network Design
A network topology dictates how data flows within a network. It defines the relationships between network devices and how they communicate. Choosing the appropriate topology is a critical decision in network design, impacting factors such as:
- Performance: How quickly data travels across the network.
- Scalability: How easily the network can expand to accommodate more devices.
- Reliability: How resilient the network is to failures.
- Security: How well the network is protected from unauthorized access.
- Cost: The overall expense of implementing and maintaining the network.
There are several key aspects to consider when discussing network topologies:
- Physical Topology: This refers to the actual physical arrangement of cables and devices. For example, the placement of computers and the way they are connected by cables.
- Logical Topology: This refers to the way data flows through the network, regardless of the physical arrangement. The logical topology may differ from the physical topology. For instance, a star physical topology might utilize a bus logical topology.
Common Network Topologies: A Detailed Overview
Let's examine some of the most prevalent network topologies:
1. Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, called the bus. Data transmitted on the bus is accessible to all devices. This topology is simple and inexpensive to implement, but it has significant limitations:
- Single Point of Failure: A failure in the bus cable brings down the entire network.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Increased network traffic can lead to significant performance degradation.
- Difficult Troubleshooting: Identifying the source of a problem can be challenging.
- Limited Scalability: Adding new devices requires modifying the existing bus, which can be disruptive.
2. Star Topology
The star topology is the most commonly used topology today. In this configuration, all devices connect to a central hub or switch. Data transmitted from one device is routed by the central device to its intended recipient.
Advantages of Star Topology:
- Easy Troubleshooting: Isolating problems is straightforward as the central device can pinpoint faulty connections.
- High Reliability: A failure of one device doesn't affect the rest of the network.
- Easy Expansion: Adding new devices is simple – just connect them to the central hub or switch.
- High Performance: Data transmission is generally efficient, especially with managed switches that employ features like Quality of Service (QoS).
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- Single Point of Failure (Central Device): If the central hub or switch fails, the entire network goes down. This can be mitigated using redundant switches and backup power supplies.
- Cost: The initial investment can be higher compared to simpler topologies like bus.
3. Ring Topology
In a ring topology, each device connects to exactly two other devices, creating a closed loop. Data travels in one direction around the ring. Each device acts as a repeater, receiving data and passing it along to the next device.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- Equal Access: Each device has equal access to the network.
- Deterministic Performance: Data transmission times are predictable.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
- Single Point of Failure: A failure in any part of the ring brings down the entire network.
- Difficult Troubleshooting: Identifying the source of a failure can be complex.
- Slow Network Expansion: Adding a new device requires breaking the ring.
4. Mesh Topology
A mesh topology involves multiple connections between devices. Each device can have multiple paths to reach other devices. This topology is characterized by redundancy, providing high reliability. There are two types of mesh topologies:
- Full Mesh: Every device is directly connected to every other device. This offers the highest level of redundancy but is expensive and complex to implement.
- Partial Mesh: Not every device is directly connected to every other device. This provides a balance between redundancy and cost.
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- High Reliability: Multiple paths ensure that communication continues even if one link fails.
- High Performance: Data can be routed through multiple paths, reducing congestion.
- Improved Security: Data can be encrypted and routed through multiple paths, making it harder to intercept.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- High Cost: Implementing a mesh topology, especially a full mesh, can be expensive due to the large number of cables and devices required.
- Complex Installation and Maintenance: Configuring and maintaining a mesh network can be challenging.
5. Tree Topology
A tree topology is a hierarchical structure that combines aspects of bus and star topologies. It is essentially a collection of star topologies connected together in a hierarchical manner resembling a tree. The root of the tree acts as a central hub or server, while other branches represent smaller star networks.
Advantages of Tree Topology:
- Scalability: It allows for easy expansion by adding new branches to the existing structure.
- Easy Management: The hierarchical structure facilitates easier management and troubleshooting.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
- Single Point of Failure: The root of the tree represents a single point of failure.
- Complex Design: Designing and implementing a tree topology can be more complex than simpler topologies.
6. Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology combines two or more different topologies. This allows for the advantages of multiple topologies to be leveraged. For example, a network might use a star topology within individual departments, which are then connected together using a bus or ring topology. Hybrid topologies are very common in larger networks.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Flexibility: It enables the adaptation of different topologies to suit various segments of the network.
- Cost-effectiveness: It can provide cost-effective solutions by employing various topologies in a manner tailored to specific needs.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Complex Configuration: Configuring and managing hybrid topologies can be more complex.
- Troubleshooting Complexity: Troubleshooting issues can be more challenging due to the integration of multiple topologies.
Choosing the Right Network Topology: Key Considerations
Selecting the best network topology depends on several factors:
- Size and Scale of the Network: Small networks might benefit from simple topologies like bus or star, while larger networks might require more complex topologies like mesh or hybrid.
- Budget: The cost of implementing and maintaining a network varies considerably across different topologies.
- Reliability and Redundancy Requirements: Networks with high reliability requirements might necessitate topologies like mesh.
- Performance Needs: If high performance is critical, then topologies that minimize bottlenecks like star are preferred.
- Scalability: The ability to easily expand the network is a critical consideration. Star topologies are generally more scalable.
- Management Complexity: Complex topologies like mesh require more sophisticated management tools and expertise.
Network Topology and Protocols: A Synergistic Relationship
The chosen network topology significantly influences the network protocols used for data communication. For example, a ring topology might utilize token-ring protocols, while star topologies are frequently used with Ethernet protocols. The interplay between topology and protocols is crucial for optimal network performance and stability. Understanding these relationships is essential for effective network design and management.
Beyond the Basics: Wireless and Cloud Considerations
The discussion of network topologies typically focuses on wired networks. However, wireless networks also have their own topological considerations. Wireless topologies, such as infrastructure mode (where wireless devices connect to a central access point) and ad-hoc mode (where devices directly communicate with each other without a central access point), have their own implications for performance, scalability, and security. Additionally, cloud computing adds another layer of complexity, as networks often integrate cloud services, requiring consideration of the topology's interaction with cloud-based resources.
Conclusion: Mastering Network Topologies for Effective Network Management
The way a network is configured, its topology, is a fundamental aspect of network design and management. Understanding the various types of network topologies—bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid—is crucial for choosing the most appropriate architecture for a given network's requirements. Careful consideration of factors such as size, budget, reliability, performance, scalability, and management complexity will guide the selection process. By understanding these concepts, network administrators can build efficient, reliable, and secure networks that effectively support their organizational needs. This understanding extends beyond merely choosing a topology; it encompasses the interplay between topology and protocols, as well as the complexities introduced by wireless and cloud technologies. Mastering network topologies is essential for achieving optimal network performance and long-term success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
One Problem Associated With Stereotypic Behavior Is It
Sep 11, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Cycloaddition Reactions Is True
Sep 11, 2025
-
What Is The Magnification Of Ocular Lens
Sep 11, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Used To Control Bleeding
Sep 11, 2025
-
Who Signs Diploma When Students Graduate From Gallaudet
Sep 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Way A Network Is Configured Is Called The _____. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.