The Index Is The ____________ Of A Piece Of Data.
circlemeld.com
Sep 20, 2025 · 6 min read
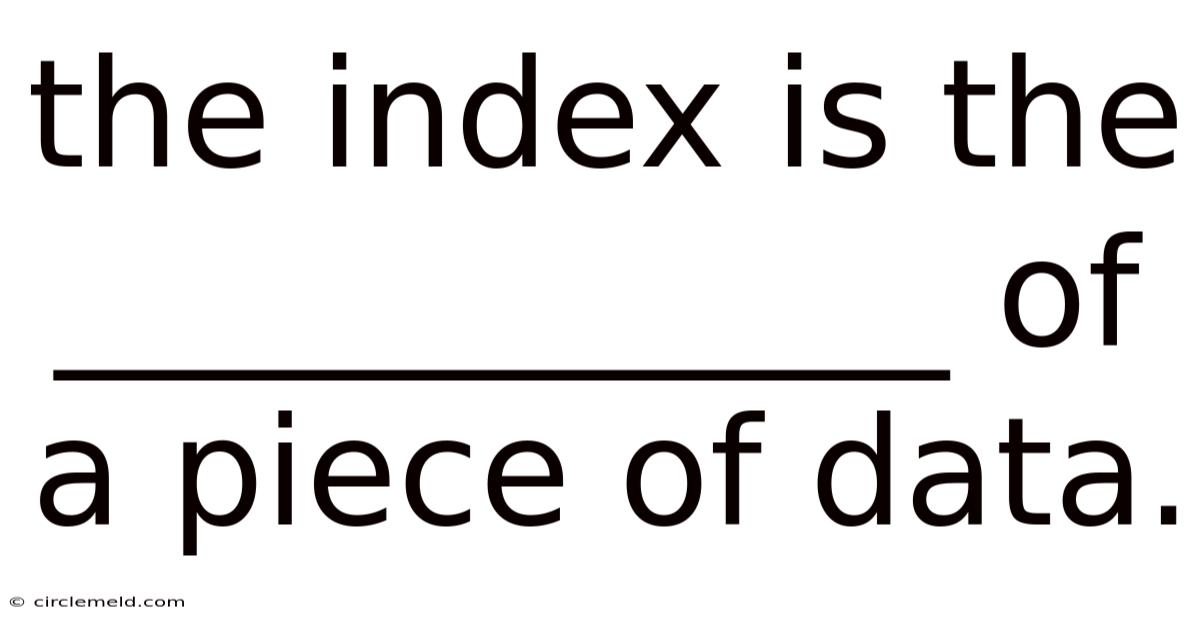
Table of Contents
The Index is the Key to a Piece of Data
Finding specific information within massive datasets can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. This is where the concept of an index becomes invaluable. The index is the key to a piece of data, providing a quick and efficient way to locate it without having to search through every single element. This article will explore the crucial role of indices in data management, explaining what they are, how they work, their different types, and their applications across various fields. Understanding indices is crucial for anyone working with databases, data analysis, or large datasets in general.
Understanding Indices: A Deep Dive
At its core, an index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Imagine a library’s card catalog: instead of searching through every book on every shelf, you can quickly find a book by its title or author using the catalog. The catalog acts as an index, mapping book titles and authors to their locations on the shelves. Similarly, a database index maps values of one or more columns to the rows containing those values.
Indices are particularly vital when dealing with large datasets where searching linearly (checking each element one by one) becomes incredibly time-consuming. Without an index, the database would have to perform a full table scan, examining every row to find the desired data. This process is extremely inefficient, especially with millions or billions of records. Indices, therefore, offer significant performance improvements by drastically reducing search time.
How Indices Work: The Mechanics Behind the Speed
The magic of an index lies in its organized structure. Different types of indices use different underlying data structures, but the general principle remains the same: to provide a shortcut to the data. A common type is the B-tree index, a self-balancing tree data structure that allows for efficient insertion, deletion, and searching of data.
When a query is executed, the database engine first checks the index. The index contains pointers to the actual data rows, allowing the database to jump directly to the relevant location instead of performing a full table scan. This process dramatically speeds up query execution, especially for complex queries involving multiple conditions or joins.
For example, let’s say you have a table of customer information with millions of entries. If you want to find all customers from a specific city, the database would have to check every row without an index. However, if you have an index on the "city" column, the database can quickly locate the relevant entries in the index and then access the corresponding rows in the table.
Types of Indices: Tailoring the Index to Your Needs
Different types of indices cater to different query patterns and data structures. Choosing the right index is crucial for optimal database performance. Some common types include:
-
B-tree index: As mentioned earlier, this is a common type used for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion. It is suitable for various query types, including range queries (e.g., finding all customers with ages between 25 and 35).
-
Hash index: This type uses a hash function to map data values to index entries. Hash indices are extremely fast for exact matches but are not suitable for range queries.
-
Full-text index: These indices are specifically designed for searching text data, allowing for efficient searching based on keywords and phrases. They are commonly used in search engines and document management systems.
-
Spatial index: Useful for geographic data, spatial indices allow for efficient searching based on location. They are used in applications such as GIS and mapping systems.
-
Unique index: This type ensures that all values in the indexed column are unique. It prevents duplicate entries and is often used for primary keys.
-
Composite index: A composite index is created on multiple columns, enabling efficient querying based on combinations of those columns. This is particularly useful for queries involving multiple
WHEREclauses.
When to Use Indices: Balancing Costs and Benefits
While indices significantly improve query performance, they also come with some trade-offs:
-
Storage overhead: Indices require additional storage space to store the index data structures.
-
Write overhead: Updating data requires updating the indices as well, leading to increased write times. This is especially noticeable with frequently updated data.
Therefore, careful consideration is needed before adding an index. It's crucial to analyze query patterns and identify the columns that are most frequently used in WHERE clauses. Indexing every column is generally not recommended as it can lead to unnecessary storage overhead and performance degradation during writes.
Practical Applications of Indices: Real-World Examples
The applications of indices span numerous fields:
-
Database systems: Indices are fundamental to the performance of relational database management systems (RDBMS) like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
-
Search engines: Search engines rely heavily on indices to quickly locate relevant documents based on keywords. Inverted indices are commonly used, mapping keywords to the documents containing them.
-
Data warehousing: In data warehousing, indices are essential for efficient querying of large datasets used for business intelligence and analytics.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Spatial indices are crucial for efficient querying and visualization of geographic data.
-
NoSQL databases: While NoSQL databases often employ different data models, many still utilize indices to improve query performance.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
-
Over-indexing: Creating too many indices can actually harm performance. The overhead of maintaining numerous indices can outweigh their benefits.
-
Poorly chosen columns: Indexing irrelevant columns provides no performance gain and wastes resources.
-
Ignoring composite indices: For queries involving multiple conditions, a composite index can be much more efficient than separate single-column indices.
-
Not monitoring index performance: Regularly monitoring index performance and adjusting them as needed is vital for maintaining optimal database performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between a clustered index and a non-clustered index?
- A: A clustered index physically sorts the data rows in the table based on the indexed column(s). Only one clustered index can exist per table. A non-clustered index is a separate data structure that points to the data rows; it does not physically rearrange the data. Multiple non-clustered indices can exist per table.
-
Q: How can I determine which columns to index?
- A: Analyze query logs to identify frequently used columns in
WHEREclauses. Consider columns used inJOINoperations as well. Tools like database profiling can help identify performance bottlenecks and guide index selection.
- A: Analyze query logs to identify frequently used columns in
-
Q: When should I rebuild or reorganize my indices?
- A: Over time, indices can become fragmented, leading to performance degradation. Rebuilding or reorganizing indices can restore their efficiency. The frequency of this depends on the database system and the level of data modification.
Conclusion: The Unsung Heroes of Data Management
Indices are the unsung heroes of data management, enabling efficient and rapid data retrieval. Understanding their functionality, different types, and optimal use is paramount for anyone working with large datasets. By carefully planning and implementing indices, you can significantly improve the performance of your applications, ensuring quick response times and a smoother user experience. Remember to strike a balance between the benefits of increased speed and the costs of storage and write overhead. Choosing the right indices and optimizing their usage is a critical aspect of database administration and data management best practices. Mastering this skill will dramatically improve your ability to work effectively with large and complex datasets.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 List Three Who Assist Odysseus Take Down The Suitors
Sep 20, 2025
-
Alkenes And Alkynes Are Called Unsaturated Compounds Because
Sep 20, 2025
-
Andrew Jackson Was A War Hero In What War
Sep 20, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast Dna From Rna
Sep 20, 2025
-
Which Operation On A Pwc Requires More Than Idle Speed
Sep 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Index Is The ____________ Of A Piece Of Data. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.