Insulin ______ Blood K Levels By Stimulating ______ In Cells.
circlemeld.com
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
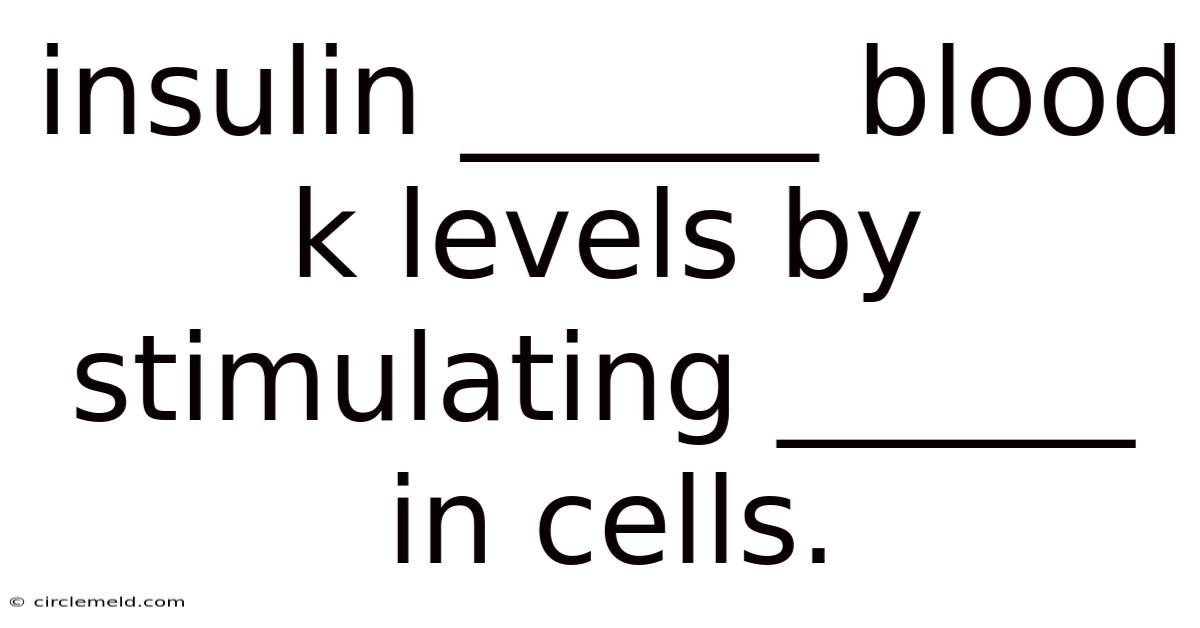
Table of Contents
Insulin's Impact on Blood Potassium Levels: A Comprehensive Overview
Insulin, a vital hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels. However, its influence extends beyond glucose homeostasis; it significantly impacts other electrolytes, most notably potassium (K+). This article delves into the intricate mechanism by which insulin lowers blood potassium levels by stimulating potassium uptake into cells. We will explore the physiological processes involved, the clinical implications of insulin's effect on potassium, and address frequently asked questions surrounding this important metabolic interaction.
Introduction: The Insulin-Potassium Connection
Maintaining proper electrolyte balance, including potassium levels, is essential for normal cellular function and overall health. Hyperkalemia (high blood potassium) and hypokalemia (low blood potassium) can both lead to serious cardiovascular and neuromuscular complications. Insulin, through its multifaceted effects on cellular metabolism, exerts a potent influence on potassium distribution within the body. Understanding this interaction is crucial for managing various medical conditions, particularly diabetes and its associated complications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex relationship, explaining the mechanisms involved and highlighting the clinical significance of insulin's effect on serum potassium.
The Mechanism: How Insulin Lowers Potassium Levels
Insulin's ability to reduce serum potassium levels primarily stems from its action on cell membranes. It achieves this through several interconnected pathways:
-
Stimulating Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump: The sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ ATPase) is a crucial membrane protein found in most cells. This pump actively transports sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and potassium ions (K+) into the cell, requiring energy in the form of ATP. Insulin enhances the activity of this pump, leading to increased potassium uptake into cells and a subsequent decrease in extracellular (blood) potassium levels. This is a significant mechanism contributing to insulin's hypokalemic effect.
-
Promoting Glucose Uptake: Insulin's primary function is to facilitate glucose uptake into cells, particularly muscle and liver cells. This glucose uptake is coupled with potassium transport. As glucose enters the cell via glucose transporters (GLUTs), it creates an osmotic gradient, drawing water into the cell. This osmotic effect indirectly facilitates potassium movement into the cell, further reducing serum potassium.
-
Increasing Cell Membrane Permeability to Potassium: Insulin also appears to influence the permeability of cell membranes to potassium ions. While the exact mechanism isn't fully elucidated, studies suggest that insulin may increase the number or activity of potassium channels in the cell membrane, allowing for more efficient potassium influx.
-
Indirect Effects via Other Hormones and Systems: Insulin's effects on potassium are not isolated. It interacts with other hormonal and metabolic pathways. For instance, insulin's impact on glycogen synthesis in the liver can indirectly influence potassium distribution. The overall metabolic shift induced by insulin contributes to the overall reduction in serum potassium.
Clinical Implications: Understanding the Significance
The relationship between insulin and potassium has significant clinical implications across various medical specialties:
-
Diabetes Management: In individuals with diabetes, especially those with poorly controlled blood sugar, hyperkalemia can be a serious concern. Insulin therapy, a cornerstone of diabetes management, helps regulate blood glucose and simultaneously lowers potassium levels. However, it's crucial to monitor potassium levels closely during insulin administration to prevent hypokalemia, a potentially dangerous complication.
-
Acute Hyperkalemia Treatment: In cases of acute hyperkalemia, which can be life-threatening, intravenous insulin administration is a critical intervention. The rapid hypokalemic effect of insulin provides a swift and effective means of lowering dangerously elevated potassium levels. This is often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as calcium gluconate and sodium bicarbonate.
-
Critical Care Medicine: Patients in intensive care units (ICUs) often experience electrolyte imbalances, and insulin's impact on potassium is crucial in their management. Careful monitoring and judicious use of insulin are necessary to prevent both hyperkalemia and hypokalemia.
-
Cardiac Conditions: Potassium levels significantly affect cardiac function. Both hyperkalemia and hypokalemia can cause cardiac arrhythmias, potentially leading to life-threatening consequences. The use of insulin in cardiac patients needs careful consideration, with close monitoring of potassium levels.
-
Surgical Procedures: Surgical procedures, particularly those involving large fluid shifts, can alter electrolyte balance. The interplay between insulin and potassium must be considered during perioperative management.
Scientific Evidence and Research: A Deeper Dive
Numerous studies have explored the intricate mechanisms and clinical implications of insulin's effect on potassium. Research using in vitro and in vivo models has confirmed the role of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump in insulin-mediated potassium uptake. Clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of insulin in lowering potassium levels in acute hyperkalemia and in managing potassium levels in diabetic patients. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of the precise molecular mechanisms and the nuances of this interaction. Advanced techniques, including molecular biology and genetic analysis, are being employed to unravel the complexity of this important metabolic pathway. This continued research is vital in improving treatment strategies for conditions associated with electrolyte imbalances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can insulin cause hypokalemia?
A: Yes, although insulin primarily lowers potassium, excessive or rapid administration of insulin can lead to hypokalemia (low potassium). This is why careful monitoring of potassium levels is crucial during insulin therapy, especially in patients at risk of hypokalemia.
Q: How quickly does insulin lower potassium levels?
A: The speed of insulin's hypokalemic effect depends on the route of administration and the dose. Intravenous insulin works relatively quickly, often within minutes. Subcutaneous insulin takes longer to take effect.
Q: What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
A: Symptoms of hypokalemia can be subtle or severe and include muscle weakness, fatigue, cramps, constipation, and palpitations. In severe cases, hypokalemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias.
Q: Are there any other factors that influence insulin's effect on potassium?
A: Yes, several factors, including the patient's overall metabolic state, the presence of other medical conditions, and the use of concomitant medications, can influence insulin's effect on potassium levels.
Q: Is it necessary to monitor potassium levels during insulin therapy?
A: Yes, especially in patients at risk of hyperkalemia or hypokalemia, regular monitoring of potassium levels is crucial during insulin therapy.
Conclusion: A Vital Hormonal Interaction
Insulin's influence on blood potassium levels is a multifaceted and crucial aspect of its overall metabolic action. By stimulating potassium uptake into cells, primarily through the enhancement of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump and the facilitation of glucose transport, insulin plays a vital role in maintaining potassium homeostasis. Understanding this interaction is paramount in the management of various medical conditions, including diabetes, acute hyperkalemia, and critical care situations. Careful monitoring of potassium levels during insulin therapy is essential to prevent both hyperkalemia and hypokalemia, ensuring patient safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes. Continued research is critical to further elucidate the complex mechanisms involved and to refine clinical strategies for managing electrolyte balance. The precise interplay between insulin and potassium highlights the intricate and interconnected nature of metabolic processes within the human body.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Economic Cost Can Best Be Defined As
Sep 21, 2025
-
Ayrshire Cow Rank In Fat Production
Sep 21, 2025
-
I Want The Not The Weather
Sep 21, 2025
-
The Alcoholic Beverages In A Private Club Are
Sep 21, 2025
-
Inattentional Blindness Can Best Be Described As
Sep 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Insulin ______ Blood K Levels By Stimulating ______ In Cells. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.